Futuristic Retro: What is a Vocoder?
A timeless voice processing effect.
What is a Vocoder? Whether you’re a trained singer or not, a Vocoder is a tool for bringing textured vocal sounds into your productions.
In this Article:
What is a Vocoder?
While the vocoder was first invented in the late 1920s, it was actually designed for the communications industry. The vocoders we know today began to emerge in the 1950s, within synthesizer designs. Subsequently, they eventually rose to popularity in the 1970s when they were used by artists like Wendy Carlos, Kraftwerk, and Electric Light Orchestra.
Over the years, some of the most notable analogue vocoder designs included:
- EMS Vocoder 5000 (1976)
- Siemens VSM 201 (1977)
- Moog 16 Channel Vocoder (1978)
- KORG VC-10 (1978)
- Roland SVC-350 and VP-330 (1979)
What is a Vocoder? : How Vocoding Works
Although there are many variations on its design, there are two basic parts to any vocoder. First, the modulator signal, which is often speech or vocals is analyzed. From there, the signal is split into various frequency bands, each with its own accompanying bandpass filter.
Meanwhile, the carrier signal, which is usually harmonic, is also sent through the same filter bank as the modulator signal. However, this is where the magic happens, as each bandpass filter adjusts itself according to the equivalent frequency band within the modulator signal.
As a result, the unique effect created imprints the harmonic content onto the modulator signal. This process allows you to imbue speech with chordal harmonics created from guitars or keyboard instruments.


What is a Vocoder? : Keyboard/Synth Vocoders
Naturally, the most interesting way to use a vocoder is as a live instrument. To do this, you’ll be speaking or singing into the microphone while playing the vocoder’s carrier signal at the same time.
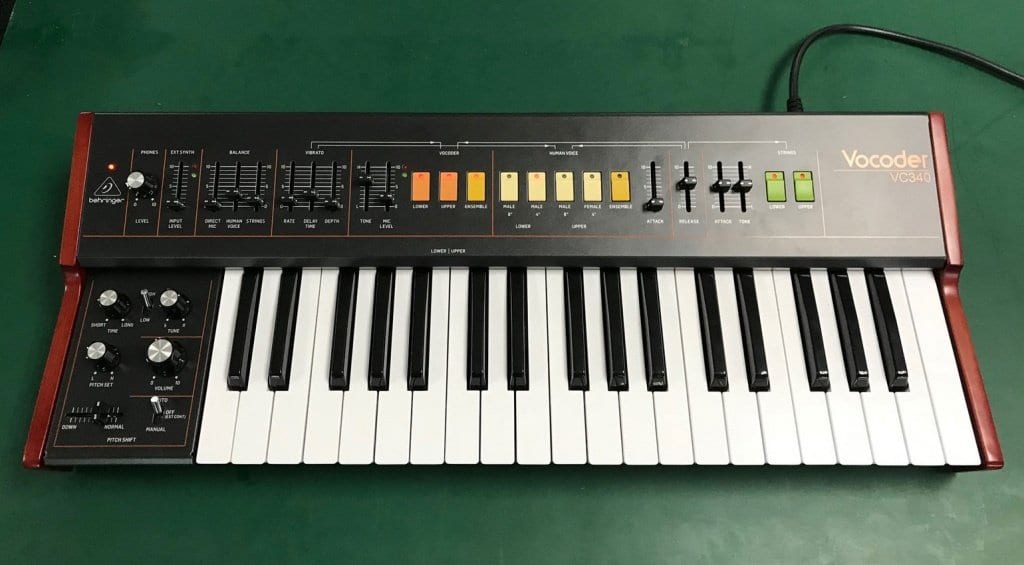

Great vocoders can be found in the form of the Behringer VC 340, the Waldorf STVC, and the microKORG series. While some of these instruments include gooseneck microphones, it’s important to note that not every vocoder has a mic preamp with gain controls.
Sending the signal from a mixer provides a preamp for your mic and allows you to optimize the gain and even make EQ adjustments to your modulator signal. This is useful if you’re using the vocoder as a solo instrument because you won’t actually hear the direct signal from your mic at all.



What is a Vocoder? : Vocoder Pedals
Vocoder pedals offer another versatile way to incorporate vocoders into your setup. Here, besides speaking or singing into the mic, you’ll have to provide the carrier signal or a MIDI signal to control the vocoder’s pitch.
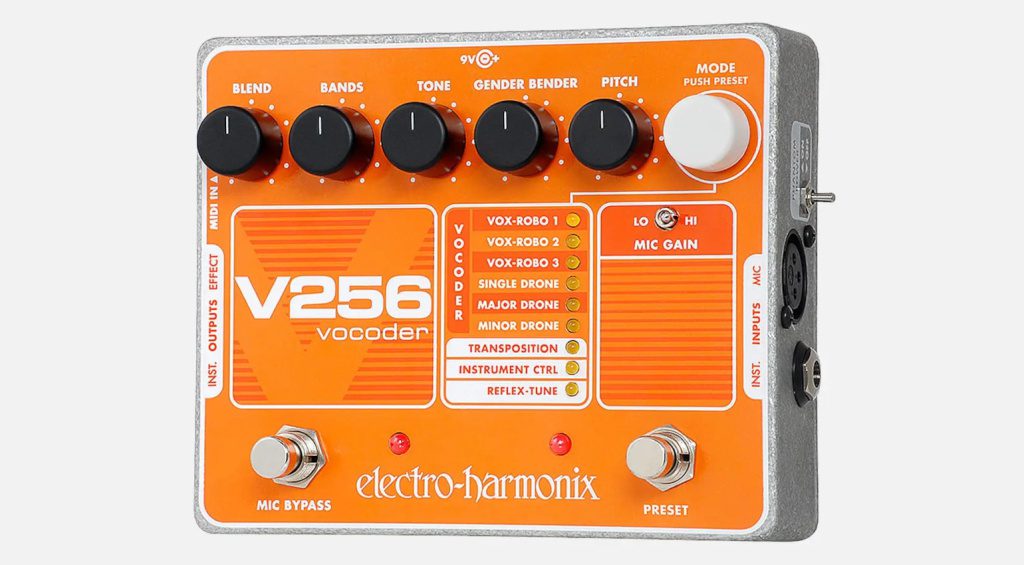

Keep in mind that, with your carrier signal, you want to use a sound that is as harmonically rich as possible to get the best results from the vocoder. To do this, try using square waves from either a synth or a distortion pedal.
One of the most basic controls common to most vocoders determines the number of frequency bands being used. As you decrease the bands, you’ll notice a reduction in resolution, as the sound becomes grainier.




What is a Vocoder? : Vocoding in your DAW
Most DAW systems have a stock vocoder plug-in, or you can easily install the free TAL-Vocoder plug-in to give any DAW the basic vintage-style vocoder sound. While some vocoder plug-ins have a built-in synthesizer to generate the carrier signal, others will require you to set this up with a sidechain signal.
To set up a vocoder synth plug-in, you open it on an instrument track in your DAW and assign the mic signal to the plug-in’s sidechain input. As you trigger MIDI notes with the mic signal present, you’ll hear the vocoder come to life.
There isn’t a right or wrong way to use a vocoder, so you can also program a chord progression and use a pre-recorded vocal signal if you have a specific idea in mind.

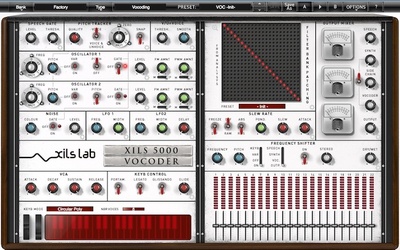
What is a Vocoder? : Eurorack Vocoders
Eurorack modules are another way to create vocoding effects, and they sound incredible. However, the filter bank modules are extremely large (around 40-50 HP) because they have to house the 16 individual bandpass filters.
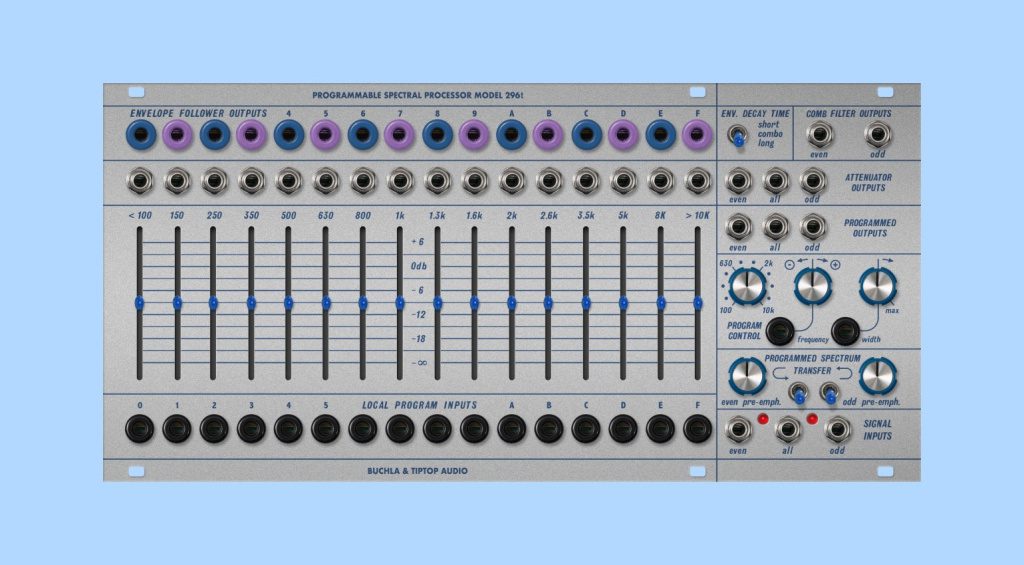

In addition, because they are designed using high-quality hand-built analogue circuitry, it pushes the price tag up considerably. If you do have the space in your Eurorack chassis, these versatile processors can be used for more than just vocoding.
Now, you can introduce the textured sound of the bandpass filter bank in any situation, be it on drums, leads, or basslines. This makes these modules a versatile creative addition to your Eurorack system, with hours of sonic fun ahead.
- Thomann’s Guide to Eurorack Modules




What is a Vocoder? : Using Non-vocal Modulators
Once you’ve got a basic feel of how a vocoder works, you can start experimenting by using modulator signals that aren’t speech or vocals. You may be limited to some degree in terms of your carrier signal, but you can use virtually anything as a modulator.
When choosing this modulator signal, it’s a good idea to keep in mind whether the sound is harmonically rich or largely atonal in character. By using rhythmic sounds that have little or no harmonic content, you can transform them with the chords you play.
A drum loop, for instance, can become something completely different with a vocoder. We can hear a great example of this used in the intro of Röyksopp’s Remind Me, where a simple drum beat becomes a highly emotive element.
More about What is a Vocoder? :
- Thomann’s Guide to Synthesizers
- All about Vocoders
- More about Music Production
*Note: This “What is a Vocoder?” article contains promotional links that help us fund our site. Don’t worry: the price for you always stays the same! We will receive a small commission if you buy something through these links. We appreciate your support!

 5,0 / 5,0 |
5,0 / 5,0 | 








